AMD is raising the performance bar once again with its next-generation Zen 5 processor. Especially the recently shared high-resolution die-shot images revealed how powerful the Zen 5 architecture is. Here are the details…
AMD Granite Ridge Zen 5 specifications
Zen 5 comes with significant innovations compared to the previous generation Zen 4 architecture. In particular, the fact that each core has 512-bit wide floating point buses indicates that performance will increase significantly. An 8-core CCD (core complex) has 1 MB of L2 cache for each core.
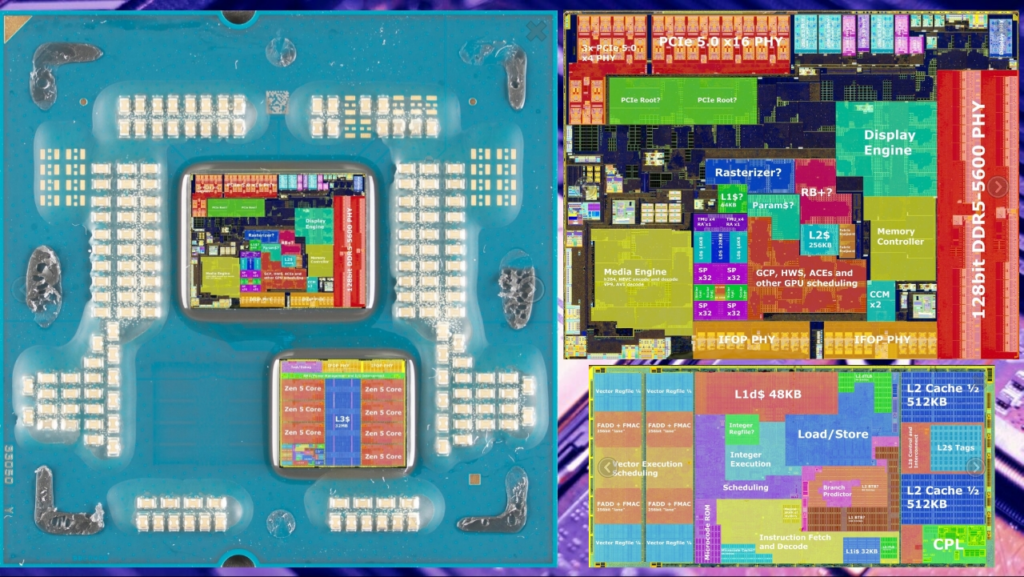
In addition, these cores share 32 MB of L3 cache, another factor that makes the processor more efficient. AMD has reportedly doubled L2 cache bandwidth and associativity with Zen 5, which means faster data processing.
Another interesting feature is that the Zen 5 processor is built on TSMC’s N4P (4 nm) manufacturing process. This means that the processor is more energy efficient and less hot. It is also said that the Zen 5 cores are physically larger than the Zen 4 cores, which is especially advantageous for intensive floating point operations.
The processor’s 32 MB L3 cache comes with support for 3D V-cache, which can be increased up to 64 MB, resulting in higher memory performance. In short, AMD Granite Ridge Zen 5 definitely comes with significant improvements in both performance and energy efficiency compared to previous generations.
AMD’s next-generation processor should be more than enough for professional applications and games that require high processing power. What do you think about this? Let us know in the comments section below.