Apple has further expanded the Apple Intelligence features it announced with iOS 18 with iOS 26. Apple has adopted a different approach than its competitors regarding data privacy, one of the most debated aspects of these AI-powered systems. The company stands out with its various security measures regarding the processing, storage, and system architecture of user data.
How does the new AI system differ from others?
At the core of Apple Intelligence are large language models that run natively on the device. Therefore, only certain models can benefit from these features. On the iPhone side, only the iPhone 15 Pro and iPhone 16 series are supported.
For iPads and Macs, devices with M1 chips are included. This limitation is due to hardware reasons. 8 GB of unified memory is required to run the AI model on the device, meaning only certain models can handle it.
Thanks to the use of the native model, actions are completed without leaving the device. With this system, Apple runs most of the Apple Intelligence features, such as notification summaries and Genmoji, directly on the device.
This allows users’ requests and personal data to be processed locally without reaching Apple servers. However, not all processing occurs on the local device. For more demanding requests, Apple’s Private Cloud Compute system comes into play.
The Private Cloud Compute system is designed to process cloud-based requests. While limited in use during iOS 18, this system became more widespread with iOS 26. Features like Siri Shortcuts can now send commands to Apple’s cloud models.
Apple announced that this system is designed not to store user data and that the necessary software images have been released to allow independent researchers to audit this.
This allows verification of whether the system actually accesses user data. With this transparency policy, Apple offers a remarkable level of security among server-based AI systems across the industry.
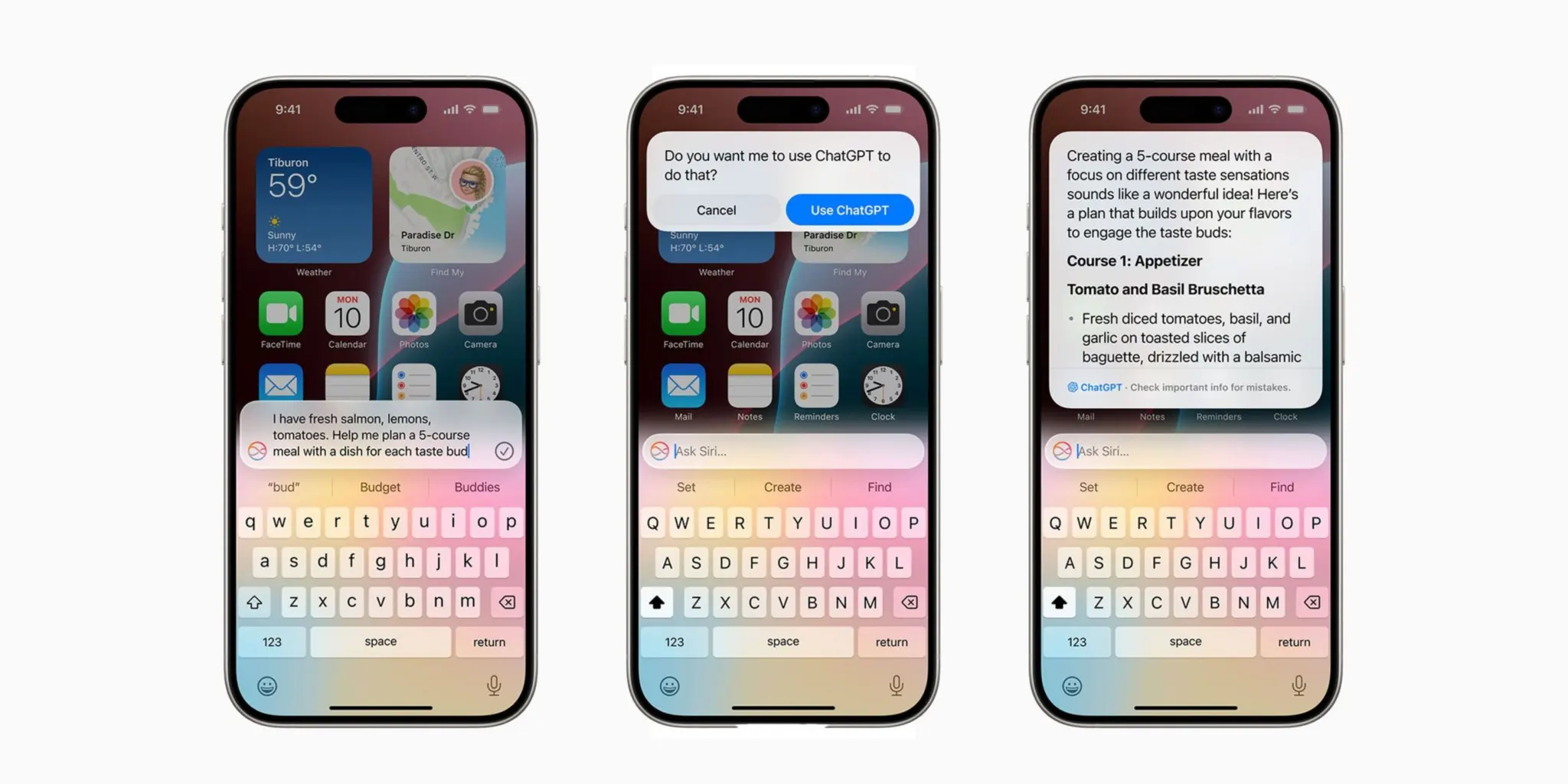
One of Apple’s privacy measures relates to ChatGPT integration. ChatGPT, accessed via Siri, does not store user data, thanks to a special agreement with Apple, and this data is not used for model training.
Furthermore, no requests are sent to ChatGPT without explicit user consent. Because Apple uses Zero Data Retention APIs in this process, OpenAI doesn’t keep any data. While the issue of user data retention was raised in the New York Times’ lawsuit against OpenAI last month, Apple isn’t affected by this practice.













