Tech enthusiasts are buzzing as a groundbreaking overclocking feat shakes the CPU world. A skilled overclocker pushed Intel’s i9-14900KF processor to an astonishing 9.12 GHz, setting a new performance record. This incredible milestone highlights the raw potential of Intel’s latest hardware and the limits of extreme cooling technology.
How the Overclocking Record Happened
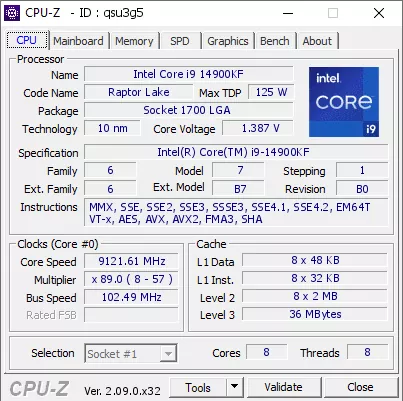
The achievement came during a session of extreme overclocking. The overclocker utilized liquid nitrogen cooling, a technique commonly used to maintain ultra-low temperatures. This cooling method prevented the processor from overheating while it operated at unprecedented speeds.
The Intel i9-14900KF, part of Intel’s Raptor Lake Refresh lineup, already boasts impressive base clock speeds and multi-core performance. However, the overclocker unlocked new heights by fine-tuning voltage settings and pushing the chip far beyond factory specifications.
Why This Record Matters
This 9.12 GHz milestone solidifies Intel’s dominance in the high-performance CPU market. It also underscores the brand’s potential for enthusiasts seeking cutting-edge performance. Gamers, developers, and tech experts view these achievements as a benchmark for what future hardware might offer.
“Intel’s i9-14900KF is already an overclocker’s dream,” said tech analyst Robert Hayes. “This record demonstrates just how far skilled enthusiasts can go with the right tools.”
The Role of Liquid Nitrogen
Achieving this record required temperatures below minus 100 degrees Celsius. Liquid nitrogen plays a crucial role in extreme overclocking by stabilizing temperatures under such high loads. Without it, traditional cooling methods like air or water would fail to handle the intense heat.
Challenges of Overclocking
Overclocking to such extremes is not without risks. Processors face the danger of permanent damage if pushed too hard. Successful overclocking also demands deep technical knowledge and access to specialized equipment.
The record-setting overclocker reported using a high-end motherboard and high-speed RAM to support the Intel processor. These components ensured stability during the intense process, reducing the risk of crashes.
Future Implications
This achievement sets the bar for future overclocking competitions. Enthusiasts may now focus on breaking the 10 GHz barrier. Meanwhile, manufacturers like Intel will likely use these feats to market their processors to performance-hungry users.















