While smartphones are at the center of our daily lives, some habits we unconsciously make silently shorten the life of these valuable devices. Electronic engineers and material scientists analyzed the common mistakes made by phone users and revealed which behaviors cause permanent damage to our devices. The scientific reasons behind these habits are directly related to the basic physics principles of phone technology.
Habits that end phone life!
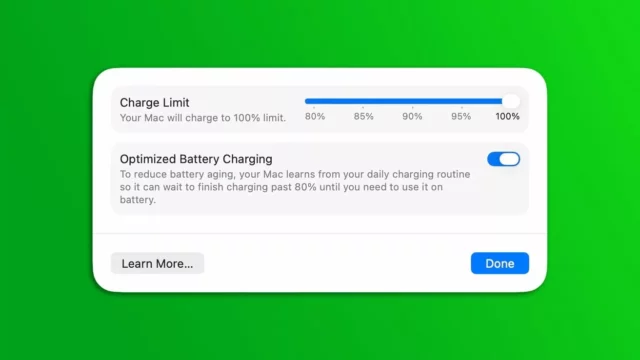
Wrong charging habits are shown as the number one cause of phone death. The biggest mistake most users make is leaving the phone on charge overnight. Lithium-ion batteries experience degradation in their electrode materials when exposed to continuous charging voltage at full charge. According to research by Dr. Yi Cui from Stanford University, keeping the battery at a charge level of 80-90 percent minimizes chemical stress factors.

Overdischarging disrupts battery chemistry. When the battery level drops below 5 percent, irreversible crystal structure changes occur in the anode and cathode materials. The ion conductivity in the electrolyte solution decreases and the battery capacity decreases permanently. Researchers from MIT have shown that full discharge cycles shorten battery life by 60 percent.
Excessive use of fast charging technologies creates thermal stress. Systems such as Qualcomm Quick Charge or USB Power Delivery shorten charging times with high voltage and current, but the heat generated during this process deteriorates the electrolyte material inside the battery. At temperatures above 45°C, the protective film called the SEI layer deteriorates, jeopardizing battery safety.
Extreme temperature conditions affect phone hardware at the molecular level. Phones left in vehicles in the summer are exposed to temperatures of 60-70°C. At these temperatures, the crystal structure of semiconductor materials deteriorates, and thermal expansion cracks form at solder points. According to data from chip manufacturer TSMC, continuous exposure to high temperatures can shorten processor life by 50 percent.
Cold weather conditions also damage electronic components. At temperatures below zero degrees, the battery electrolyte approaches freezing point, dramatically decreasing ion mobility. Liquid crystal molecules in LCD screens slow down at low temperatures, deteriorating image quality. Capacitors and resistors lose their electrical values with temperature changes.
Physical impacts and drops cause micro cracks. The G-forces that the phone is exposed to when it falls to the ground break the solder connections. Microscopic damage occurs especially at the connection points of the processor and memory chips to the motherboard. Although this damage is not noticed at first, it leads to connection failures over time.
Using the wrong charger causes voltage fluctuations. Non-original adapters send inappropriate voltage and current values to the phone. The power management chip, called the power management unit, burns out when constantly exposed to excessive voltage. Chargers that do not comply with IEEE standards also create electromagnetic interference and disrupt sensitive RF circuits.
Excessive multitasking and gaming increase processor temperature to critical levels. The simultaneous operation of the CPU and GPU at high performance activates the protection mechanism called thermal throttling. However, continuous high temperatures create electromigration in the transistor structures on the chip. In this process, metal conductors change places at the atomic level, causing permanent performance losses.
The habit of not using a case causes static electricity damage. Static electricity accumulated in the human body creates a sudden voltage increase when the phone is touched. ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) damage burns sensitive circuits, especially in the USB port and headphone jack. Protective cases provide insulation against these electrical discharges.
Using the phone in humid environments initiates corrosion processes. Water vapor causes oxidation in the metal parts inside the phone. Moisture leaking especially from the charging port and speaker grills can cause short circuits in the circuit paths on the motherboard. Even if water damage indicators do not change, microscopic moisture gradually deteriorates electronic components.
Neglecting software updates creates performance problems as well as security vulnerabilities. Old software versions use the hardware inefficiently, causing excessive energy consumption. Updates released by Apple and Android manufacturers usually include power management optimizations. Not making these updates shortens the battery life.
Allowing the phone to get dirty disrupts heat dissipation. Dust and dirt particles block the ventilation holes in the phone case. This causes the internal temperature to increase and the thermal management system to become inadequate. Dirt accumulation, especially in the charging port and speaker areas, can cause electricalIt weakens the connections.
Keeping magnetic accessories close to the phone calibrates the sensitive sensors. Components such as Hall effect sensors, digital compasses and magnetometers can become permanently misaligned in strong magnetic fields. Magnetic wallet cases and car holders can compromise the accuracy of navigation systems.
Keeping the vibration feature constantly active causes wear on the haptic motor. Since the vibration motor is a small electric motor, it is subject to mechanical wear with constant use. When the motor brushes wear out, the vibration force decreases and eventually stops working altogether.
Keeping Bluetooth and Wi-Fi on unnecessarily causes wear on the RF emitter circuits. The constant signal search and connection processes strain the radio frequency chips. This both shortens the battery life and reduces the quality of the wireless connection over time.
Carrying phones with keys in a pocket or bag causes screen and case damage. The metal surfaces of the keys can scratch even hardened glass such as Gorilla Glass. These microscopic scratches grow over time and become the starting point for screen breakage.
Keeping the volume constantly at maximum causes the speaker coils to burn out. The thin wire coils inside the speaker heat up when excessive power is input and lose their electrical resistance. Burnt speaker coils completely cut off the sound output or cause serious distortion.
All of these habits create cumulative damage to the phone hardware. Individually seemingly harmless behaviors, when combined, cause the device to die prematurely. By developing conscious usage habits, we can significantly increase both the performance and lifespan of our phone. Modern smartphones can perform optimally for 5-7 years when used correctly.