The total solar eclipse of 2024 occurred on April 8, 2024. It was visible across parts of North America, including Mexico, the United States, and Canada. Here’s the live broadcast of NASA on Solar Eclipse 2024:
Visibility:
- A total solar eclipse happens when the moon completely blocks the sun, creating a brief period of darkness during the daytime.
- The path of totality, where the complete blockage is visible, crossed over North America from the Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast.
- People outside the path of totality could still witness a partial eclipse, where the sun appears partially covered by the moon.
Key Facts:
- This eclipse was significant because the moon was slightly closer to Earth than usual, resulting in a wider path of totality.
- It lasted for nearly 4 and a half minutes in some parts of Texas, making it a longer eclipse than the 2017 event in the US.
- Millions of people were estimated to have witnessed the eclipse in North America.
Additional Resources:
- You can find maps and information about the specific timing of the eclipse in different locations by searching online for “2024 solar eclipse path” or “NASA 2024 eclipse.”
- Here are some links that might be helpful:
What is a solar eclipse and what are the types of solar eclipses?
A solar eclipse happens when the moon comes between the Earth and the sun, casting a shadow on Earth. There are two main types of solar eclipses: total and partial.
Total Solar Eclipse:
- This is the most dramatic type of eclipse. During a total eclipse, the moon completely blocks the sun, creating a brief period of darkness during the daytime.
- The sky can darken considerably, and stars may even become visible.
- The corona, the sun’s outer atmosphere, becomes visible around the completely black disc of the moon.
- Totality, the period of complete darkness, only lasts for a few minutes at most, and the entire eclipse sequence (from partial to total and back) can take a couple of hours.
- Only observers within a narrow path on Earth’s surface, called the path of totality, can witness a total eclipse.
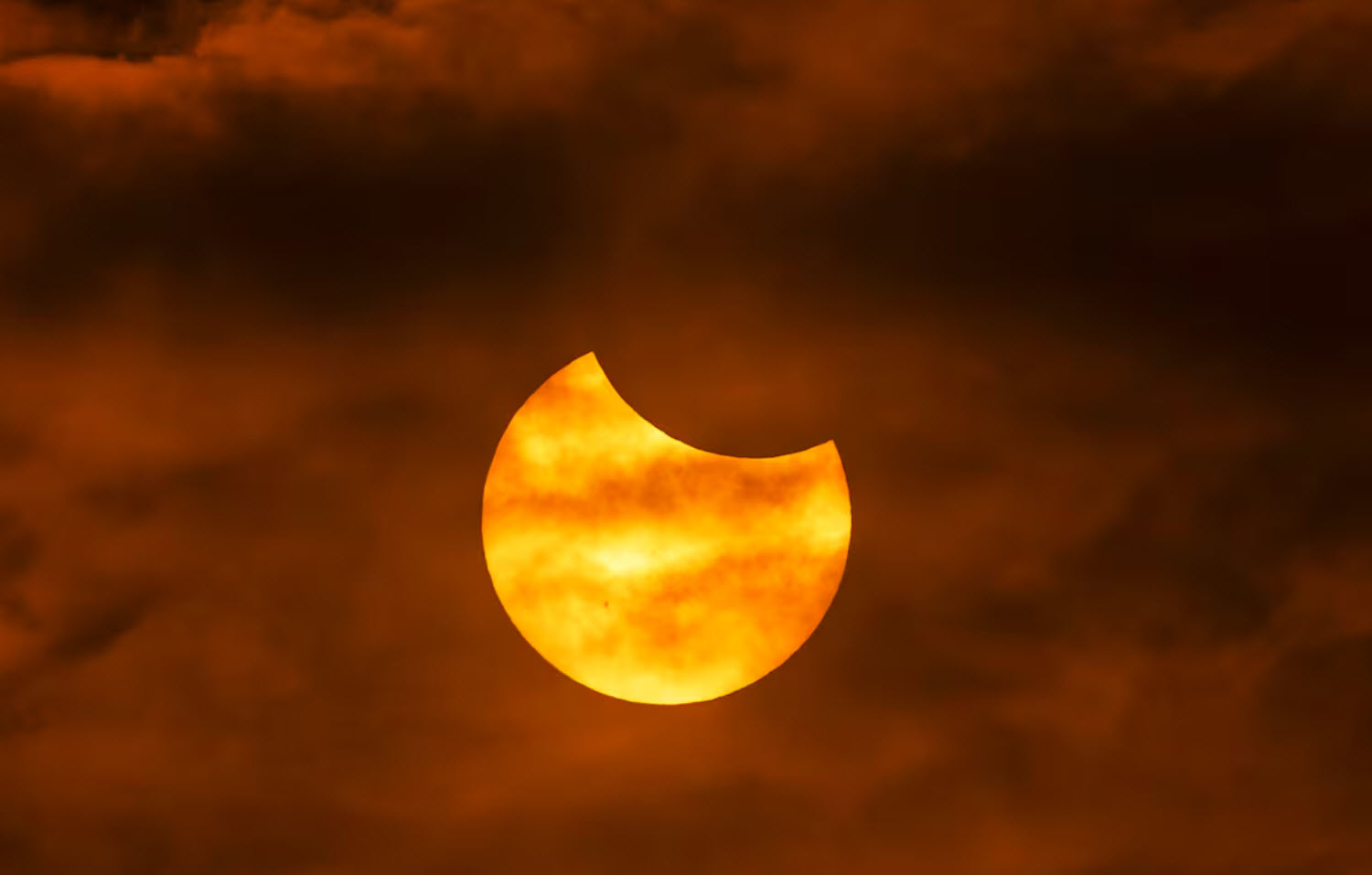
Partial Solar Eclipse:
- This occurs when the moon only partially covers the sun.
- The sun appears as a crescent or a bite is taken out of it.
- The sky might get slightly dimmer, but nowhere near as dark as during a total eclipse.
- Partial eclipses are visible from a much wider area on Earth compared to the path of totality for a total eclipse.
Here’s an analogy to help understand the difference:
- Imagine shining a flashlight on a ball (Earth) and a marble (moon) is placed between them.
- In a total eclipse, the marble completely blocks the flashlight’s beam from reaching a small spot on the ball.
- In a partial eclipse, the marble only partially blocks the beam, casting a shadow on a larger area of the ball.



 Shiftdelete.net
Shiftdelete.net